Pourpanah, F., Abdar, M., Luo, Y., Zhou, X., Wang, R., Lim, C. P., … & Wu, Q. J. (2022). A review of generalized zero-shot learning methods. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence.
#
[ 1. Introduction ]
- 기존 이미지 처리, 컴퓨터 비전 분야에서 딥러닝 모델의 발전
- feature extraction에서 classification까지 end-to-end solution을 제공하는 기능으로 인기를 얻음
- 학습을 위해 여전히 많은 양의 sample과 class에 대한 label data를 필요로 함
- 이러한 대용량의 labeled data를 수집하는 것은 어렵고 training data에 있는 class가 아닌 경우(unseen data) 분류가 불가능하다는 문제가 존재함
- 모든 class에 대한 labeling 어려움(추가적인 도메인 지식 필요)
- 다양한 학습 구성을 위한 기술
- One-shot learning
- Few-shot learning
- OSR(Open Set Recognition) : unseen class에 속하지만 정확한 class label 예측 불가
Out-of-distribution : training sample과 다른 test sample을 식별하고자 하지만 불가
- 인간은 대체로 약 3만개의 카테고리를 인식할 수 있으며, 모든 카테고리를 배우지 않고도 파악이 가능함
- 예) ‘말(horse)’을 본 적이 있는 아이는 얼룩말을 보고 ‘흑백 줄무늬가 있는 말’이라고 생각할 수 있음
→ 다른 class data sample에서 얻은 knoledge를 사용하고 sample이 거의 없는 class 처리를 위한 classification model을 공식화 함
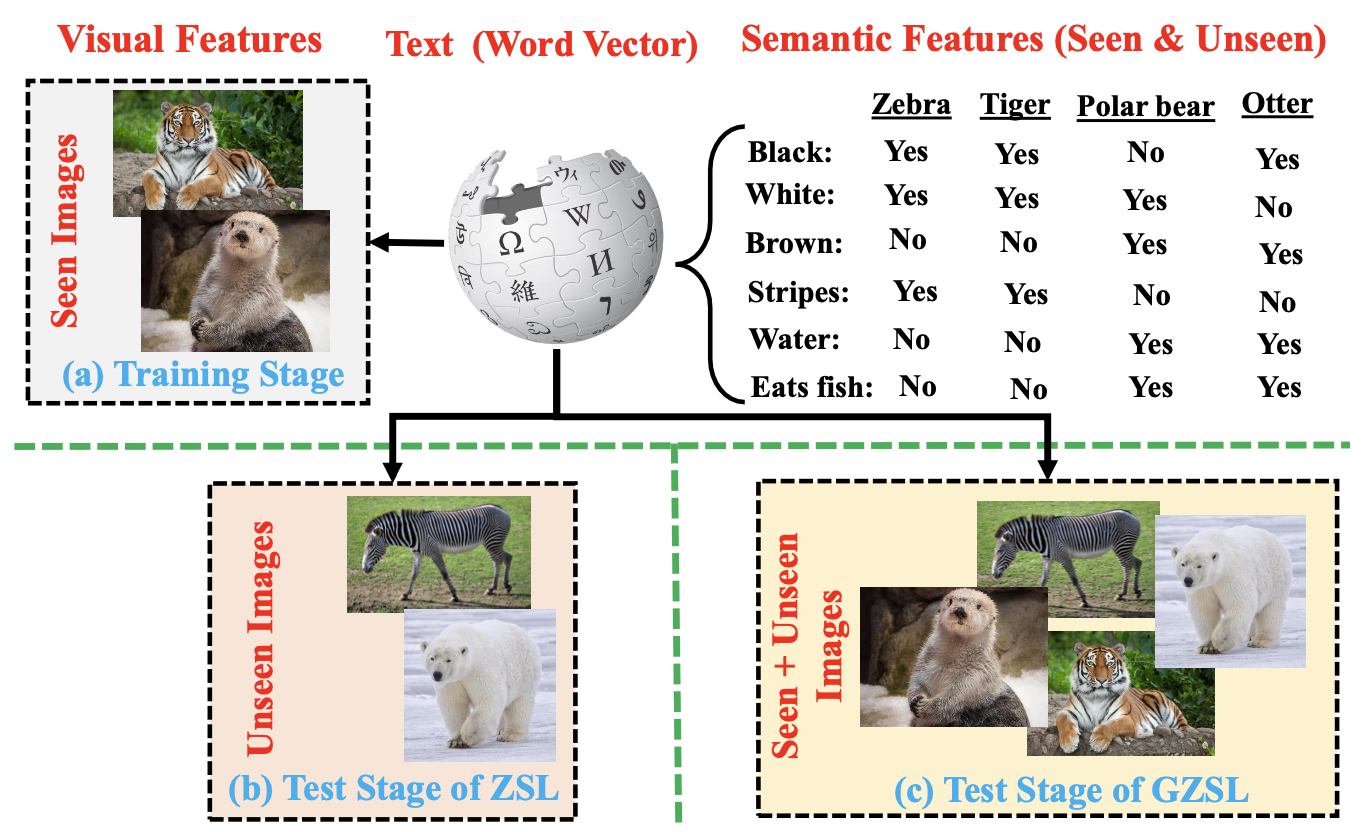
- ZSL의 목표
- seen class(source domain)로부터 얻은 transferring knowledge를 통해 unseen class(target domain)의 객체를 분류하는 학습 모델 구축
- semantic information을 사용하여 seen/unseen class 간 격차 해소
- seen, unseen class의 name을 고차원 벡터에 포함하며 아래의 벡터이거나 벡터들의 조합으로 구성
- 수동으로 정의된 attribute vector
- 자동으로 추출된 word vector
- context 기반의 embedding
- test data는 unseen class 로만 구성되지만, 실제로는 unseen class만 분류하는 것보다 seen/unseen class를 동시에 인식해야 함
⇒ “GZSL; Generalized Zero Shot Learning”
![Fig1]()
1. Contributions
- ZSL 관련 연구 논문 [3], [24], [26], [27] 와의 차이점
- [3]은 ZSL, few GZSL method에 초점을 맞춤
- [24] ZSL, GZSL method에 대해 각각 서로 다른 case study(different data set 사용) 진행했으며, ZSL, GZSL method 자체보다 empirical research에 중점을 둠
- [26] GZSL에 대한 간단한 논의 + ZSL에 초점을 맞춤
[27] COVID-19 질병을 위한 ZSL method의 중요성 강조
→ ZSL보다 GZSL에 대한 in-depth survey and analysis를 포함한 기존 논문이 존재하지 않음
⇒ 본 논문은 GZSL에 대한 포괄적인 review 제공(problem formulation, challenging issue, hierarchical categorization, applications..)을 목표로 함
- The main contributions of this review paper include:
- comprehensive review of the GZSL methods, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first paper that attempts to provide an in-depth analysis of the GZSL methods;
- hierarchical categorization of the GZSL methods along with their corresponding representative models and real-world applications;
- elucidation on the main research gaps and suggestions for future research directions.
2. Organization
섹션별 주요 내용
- Overview of GZSL
- problem formulation
- semantic information
- embedding spaces
- challenging issues
- Inductive and semantic transductive GZSL methods
- The transductive GZSL methods
- The applications of GZSL to various domains
- Discussion on the research gaps and trends for future research
- Overview of GZSL
[ 2. Overview of Generalized Zero-Shot Learning ]
1. Problem Formulation
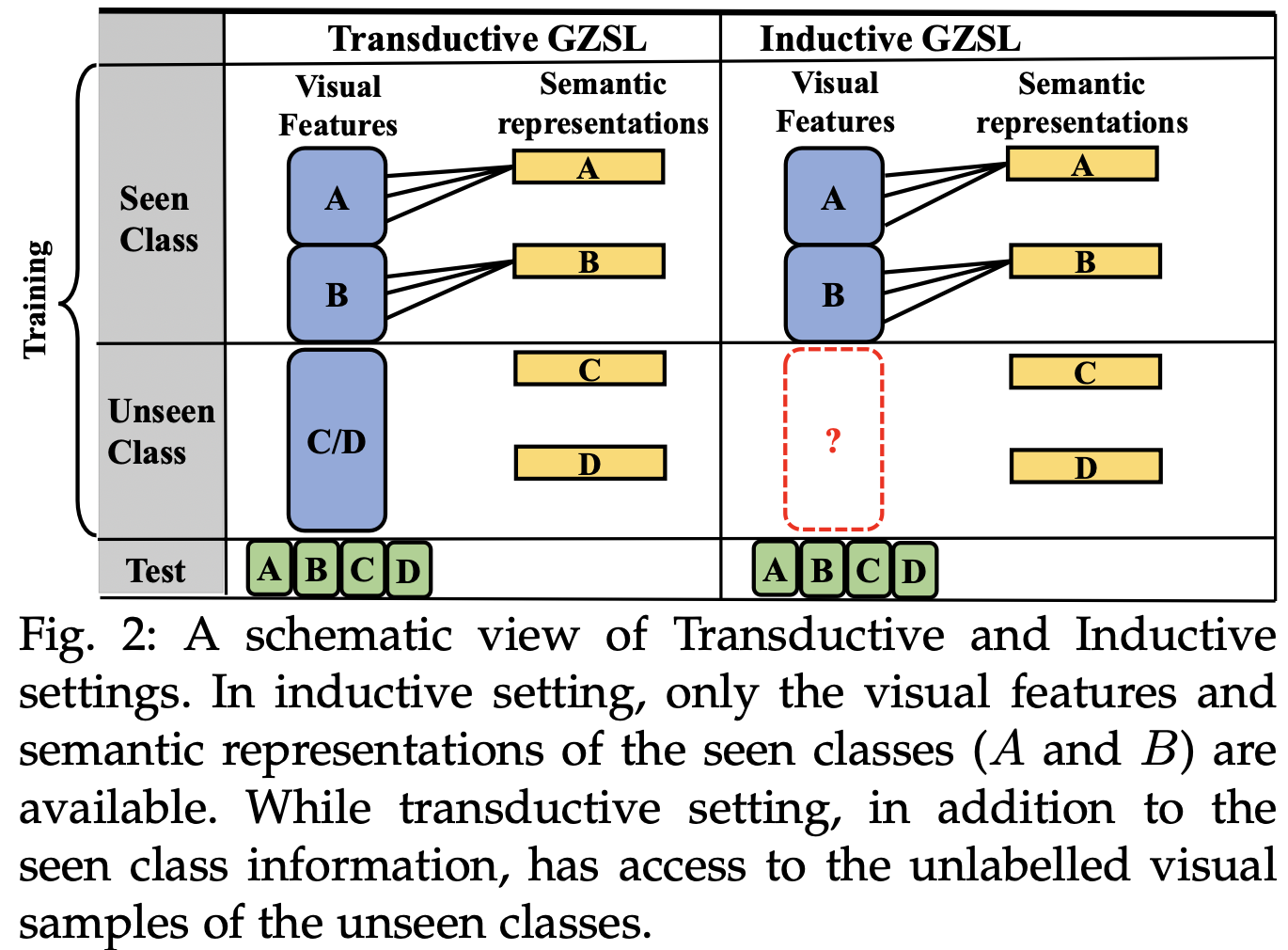
- GZSL 학습 단계
![Fig2]()
- Inductive learning
- seen class의 visual feature + semantic information 만으로 모델 구축
- Transductive learning
- unseen class의 unlabeled visual feature + semantic information 활용
- Inductive learning
2. Performance Indicators
- Accuracy of seen (Acc s)
- Accuracy of unseen (Acc u)
- Area Under Seen-Unseen Accuracy Curve (AUSUC)
- AUSUC value 높을수록 GZSL task에서 balanced performance를 달성하는 것을 목표로 함
Harmonic Mean (HM)
![math]()
- GZSL이 seen class 에 편향된 경우 ⇒ Acc s > Acc u ⇒ HM score 낮아짐
3. Semantic Information
- unseen class는 label이 없으므로 semantic information을 사용하여 seen class와 unseen class 간 관계를 구축 → ZSL에 활용
- semantic information 은 모든 unseen class의 recognition properties를 포함해야하며, 사용성 보장을 위해 feature space의 sample과 관련이 있어야 함
- 종류
- Manually defined attributes
- Word vectors
- ?.?
4. Embedding spaces
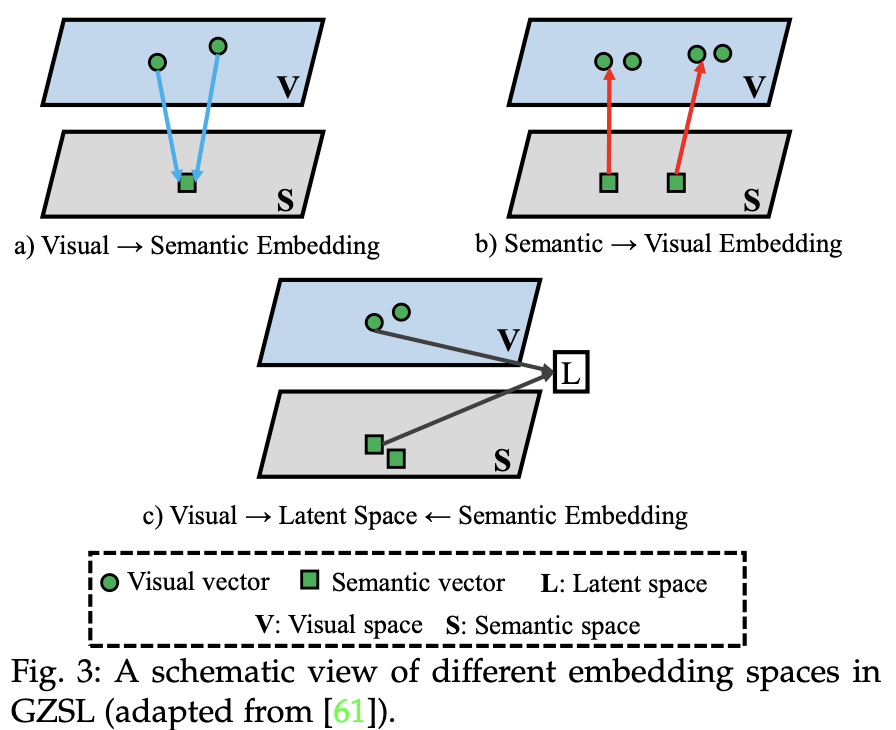
- Semantic Embedding
- class에 속하는 모든 이미지의 semantic embedding을 일부 ground-truth label embedding에 맵핑하도록 하는 것
- nearest neighbor search를 사용하여 test image 인식 가능
- Visual Embedding
- semantic representation을 해당 visual feature와 가깝게 만드는 것
- nearest neighbor search를 사용하여 test image 인식 가능
- Latent Embedding
- semantic/visual embedding space 사이의 explicit projection function을 학습하는 것은 어려움 → semantic/visual representation을 common space에 투영
- intra-class compactness, inter-class separability를 만족해야 함
5. Challenging Issues
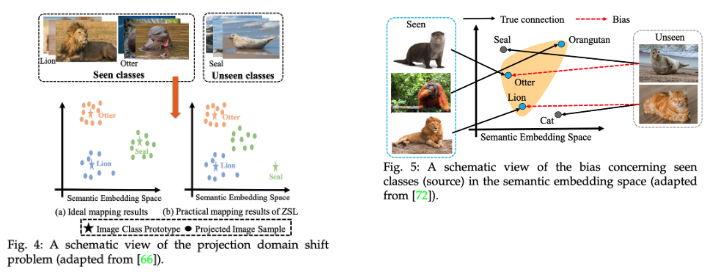
- Fig 4.
- (a) Ideal mapping result
- (b) Practical mapping result
- Fig 5.
- GZSL은 seen/unseen class 모두에 대한 인식을 수행하는 모델을 학습하므로, 일반적으로 seen class에 편향되고 unseen class data가 seen class로 잘못 분류됨
- 대부분의 ZSL은 이 문제를 효과적으로 해결할 수 없으므로, calibrated stacking, novelty detector..제안
- calibrated stacking : seen/unseen class 모두에서 균형있게 인식하도록 함
- scaled calibration & probabilistic representation 도 유사한 방법
- detector : test sample이 seen/unseen 중 어느 class에 속하는지 식별하도록 함
- calibrated stacking : seen/unseen class 모두에서 균형있게 인식하도록 함
[ 3. Review of GZSL Methods ]
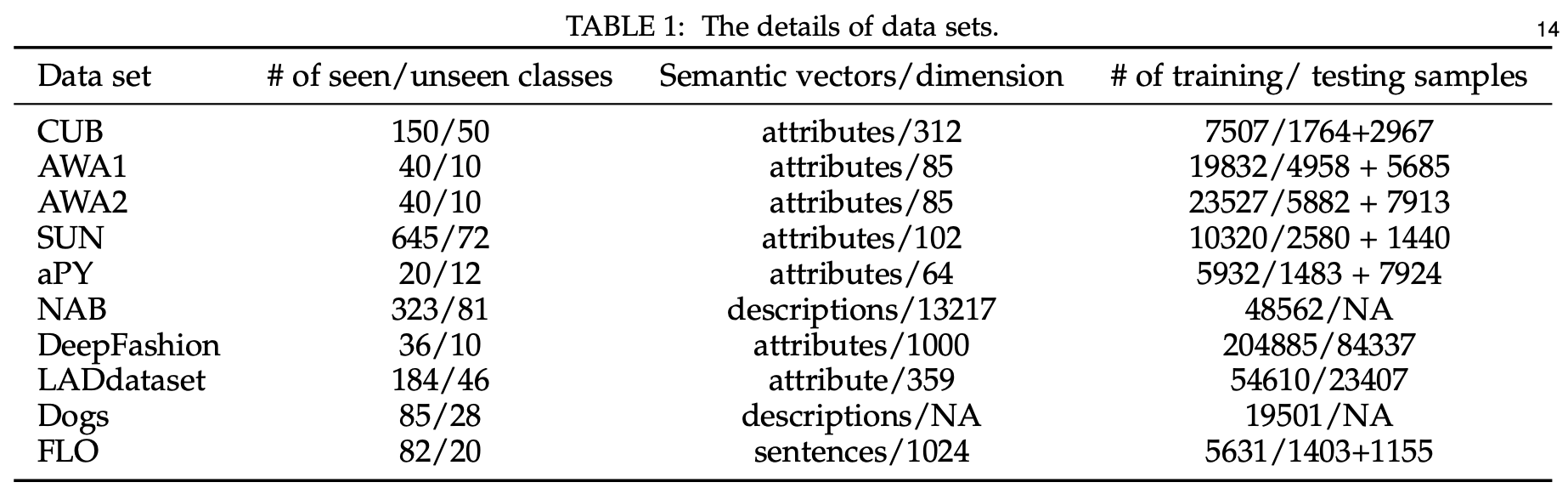
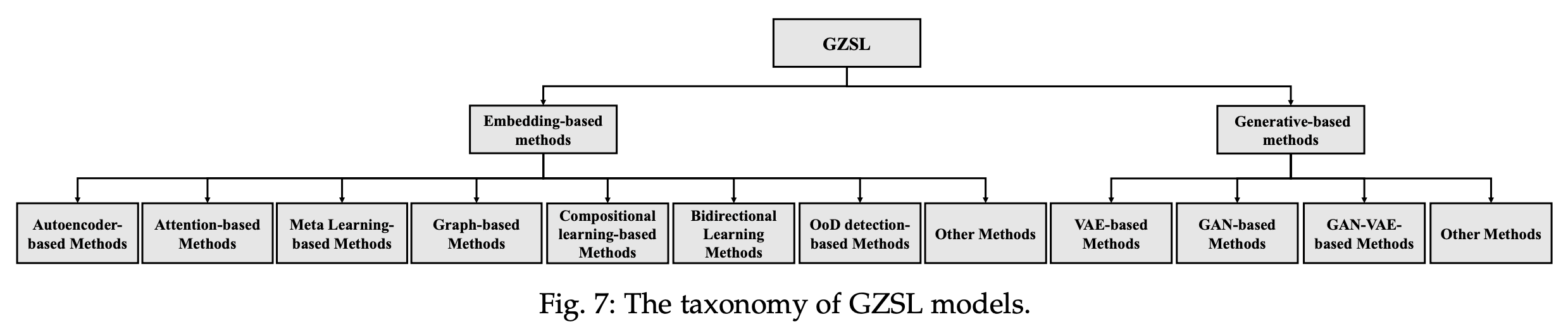
1. Embedding-based methods
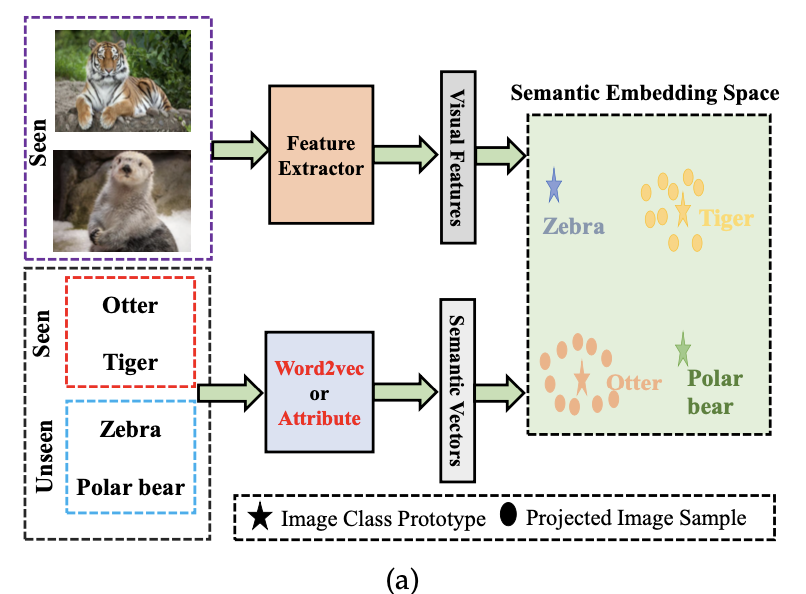
embedding space 학습 → seen class의 low-level visual feature을 해당 semantic vector와 연결
GZSL 문제를 해결하기 위한 다양한 embedding based method
![Fig7]()
Out-of-distribution Detection-based Methods
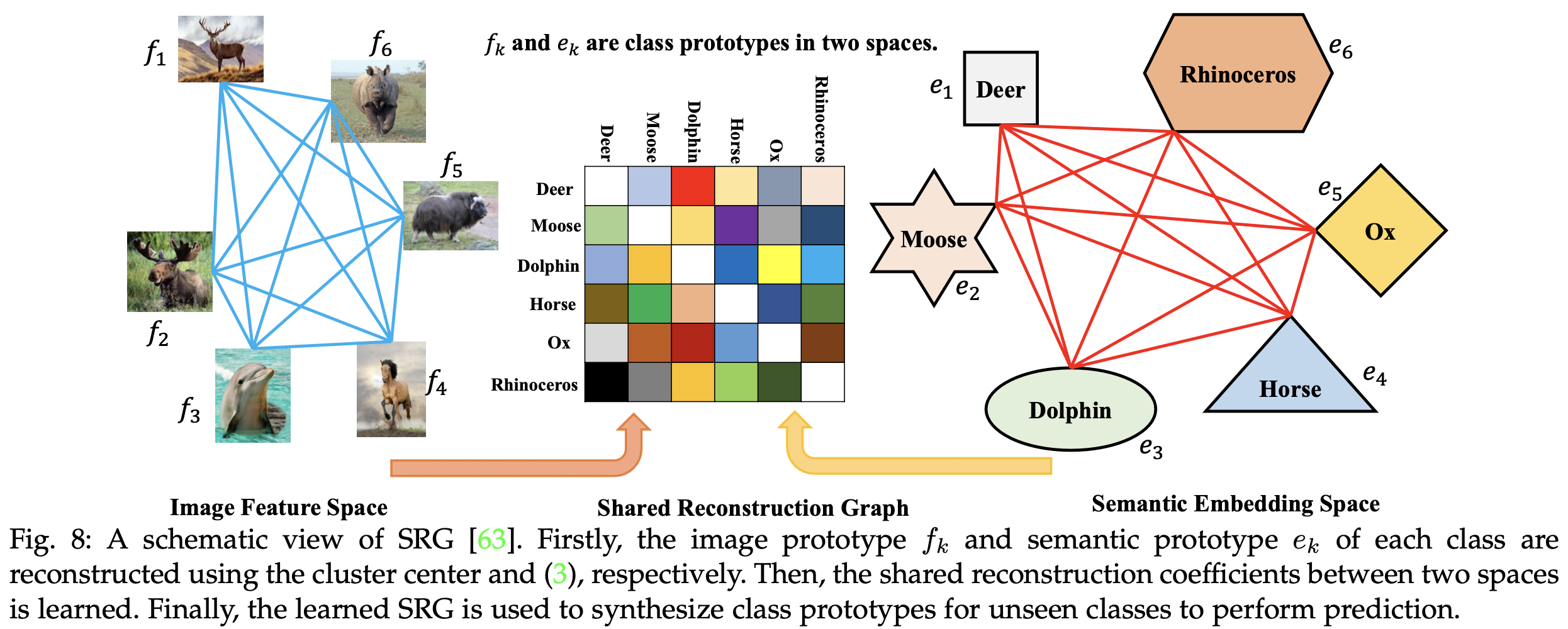
Graph-based Methods
![Fig8]()
Meta Learning-based Methods
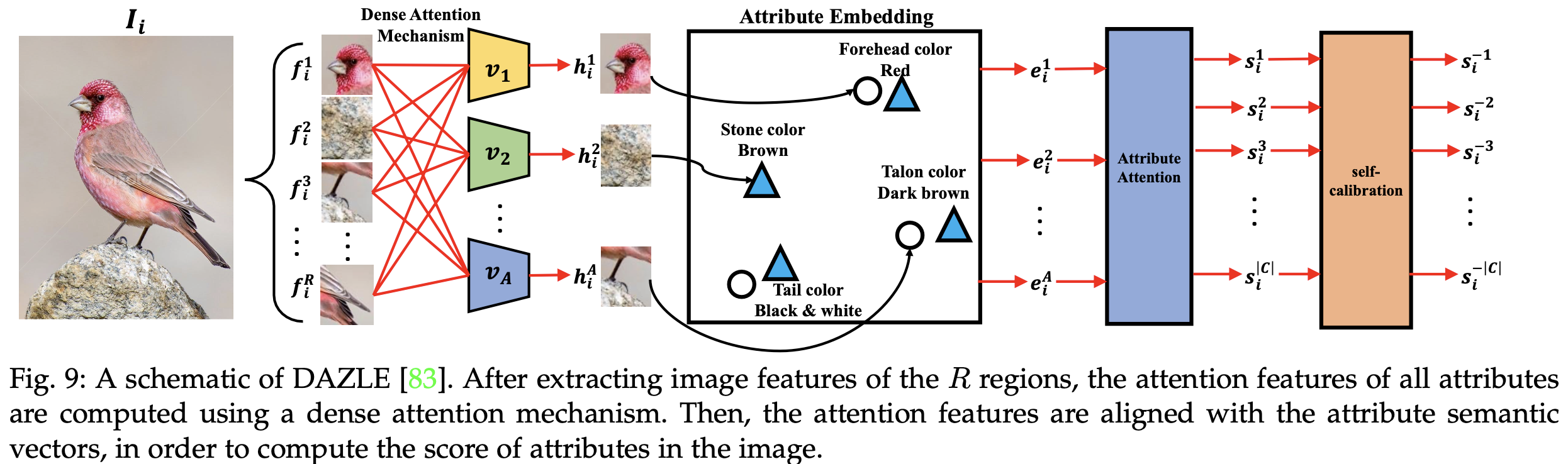
Attention-based Methods
![Fig9]()
Compositional Learning-based Methods
Bidirectional Learning Methods
Autoencoder-based Methods
Other methods
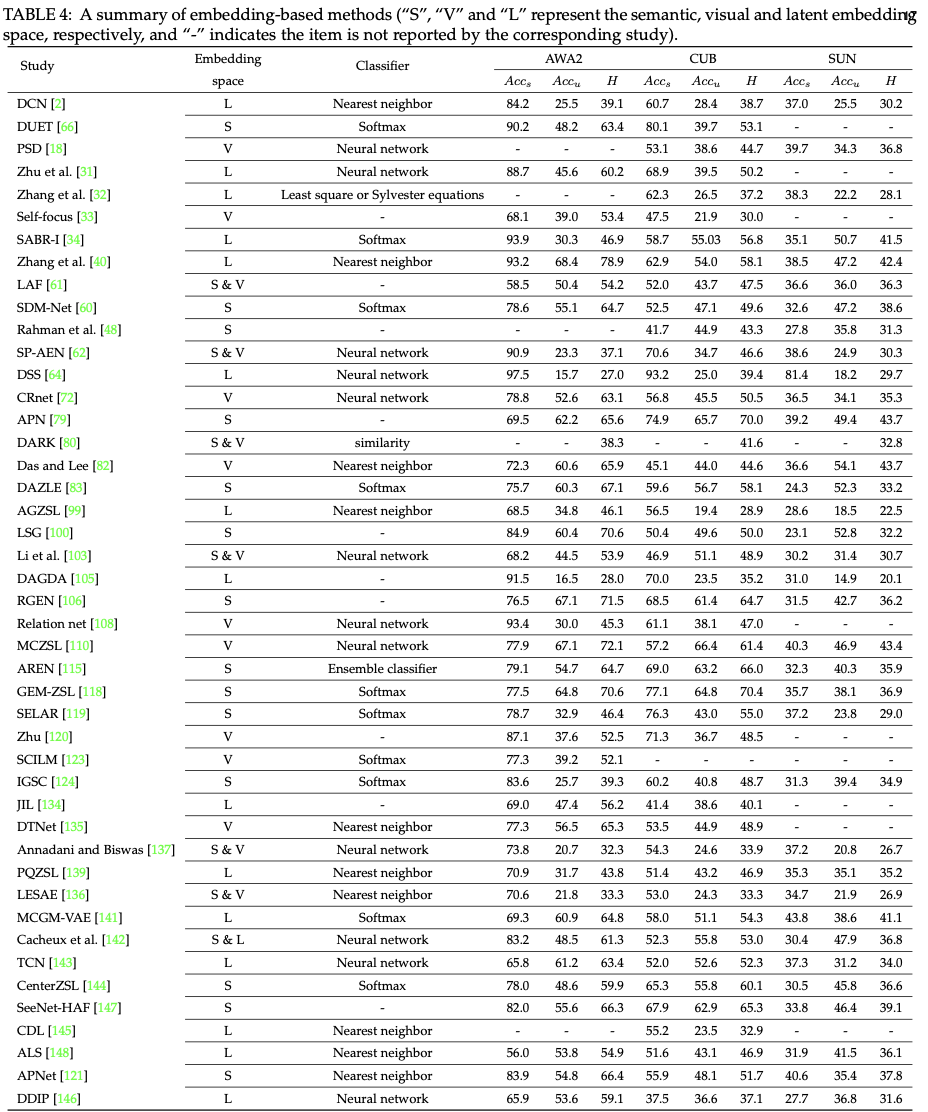
2. Generative-based methods
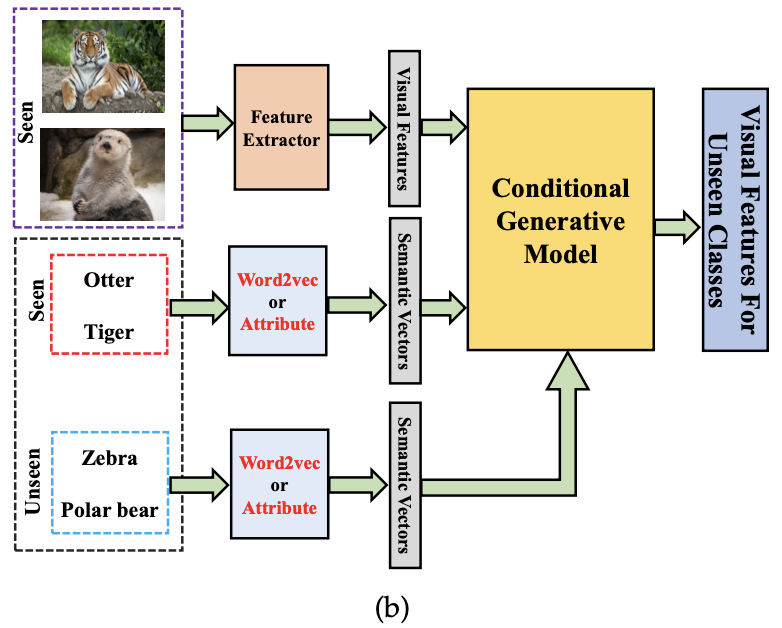
- seen/unseen class의 semantic representation을 기반으로 unseen class에 대한 image/visual feature를 생성하는 모델 학습
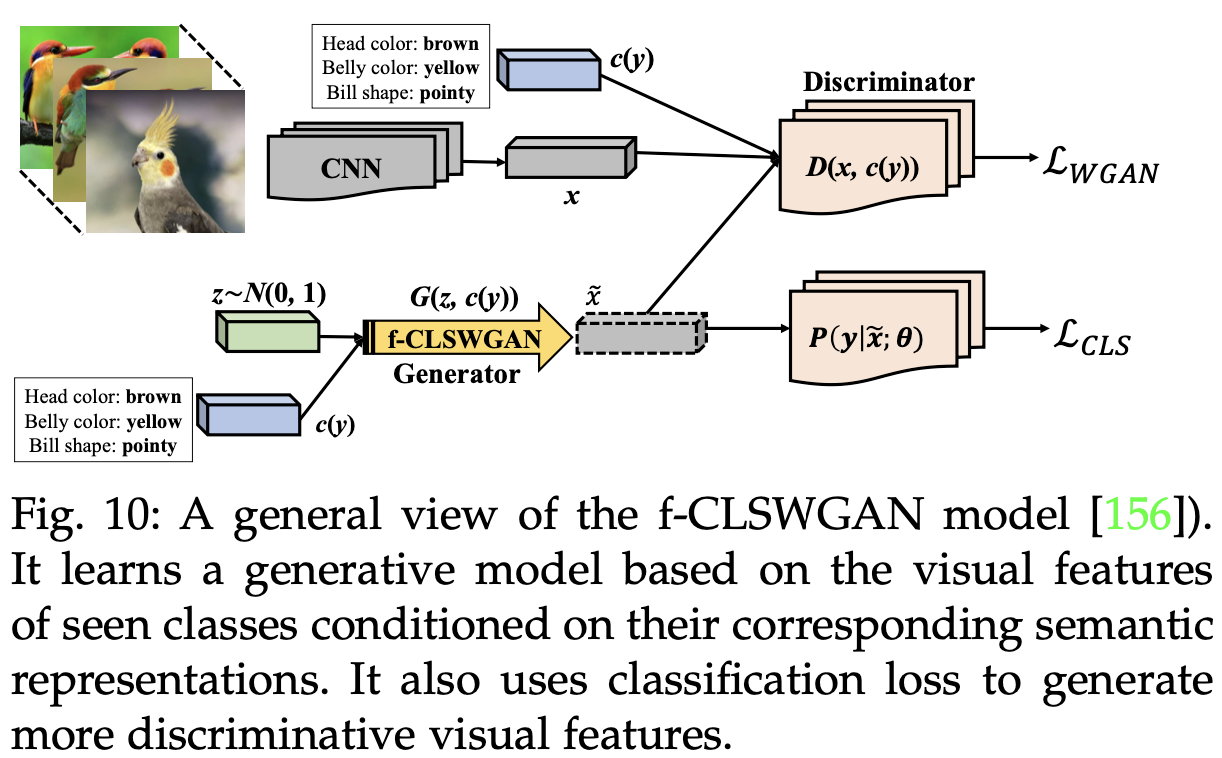
- Generative Adversarial networks
![Fig10]()
- Generative Adversarial networks
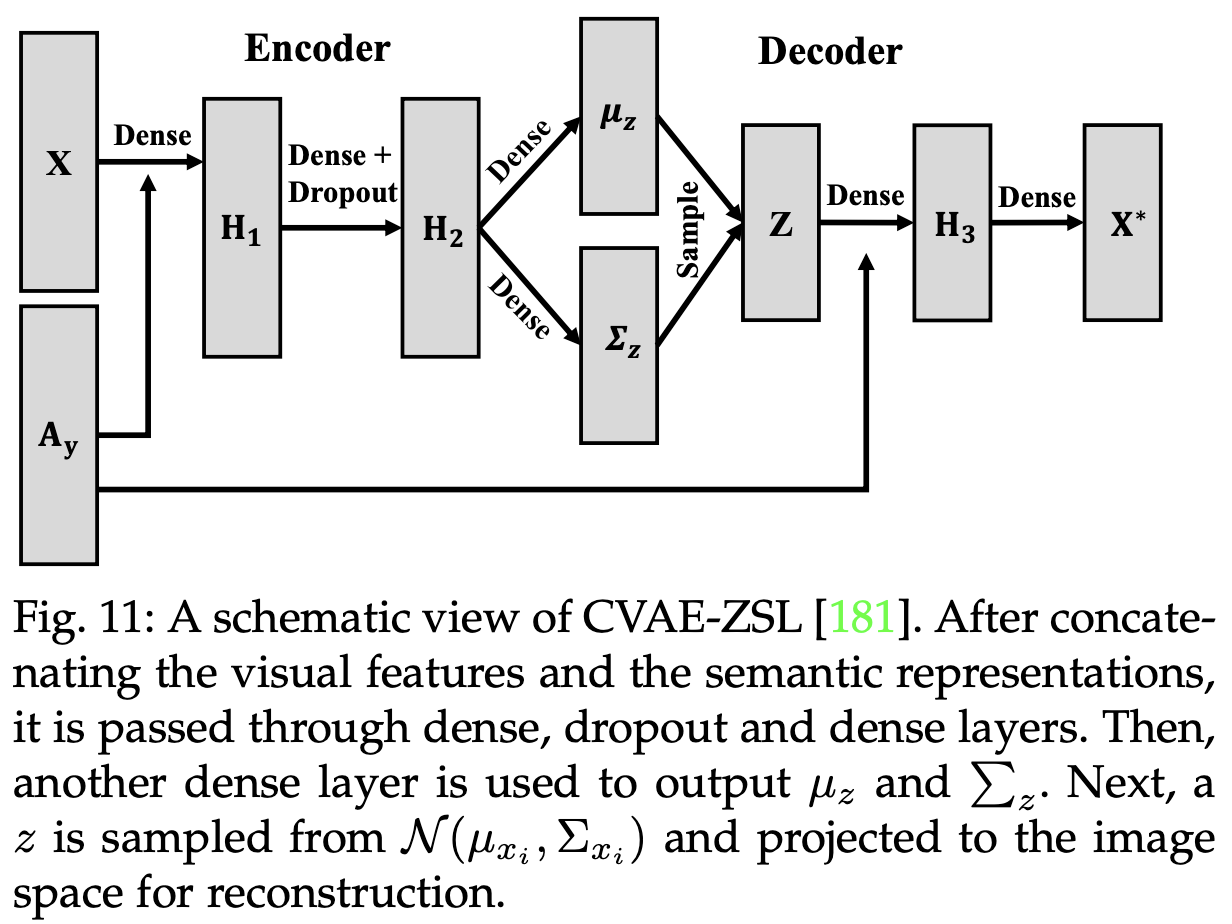
Variational Autoencoders(VAEs)
![Fig11]()
Combined GANs and VAEs
Other Methods
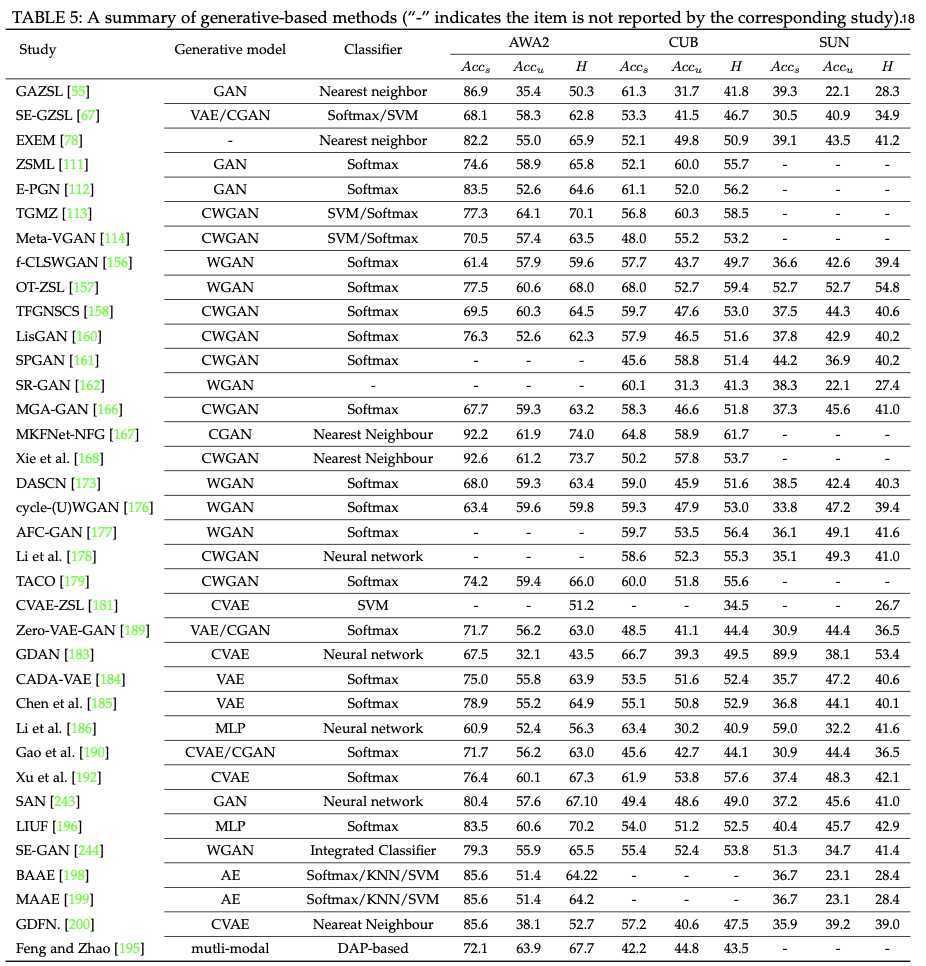
[ 4. Transductive GAZSL Methods ]
- unlabeled data에 접근 → 모델이 unseen class의 분포 파악 가능 ⇒ discriminative projection function 학습 가능
1. Embedding-based methods
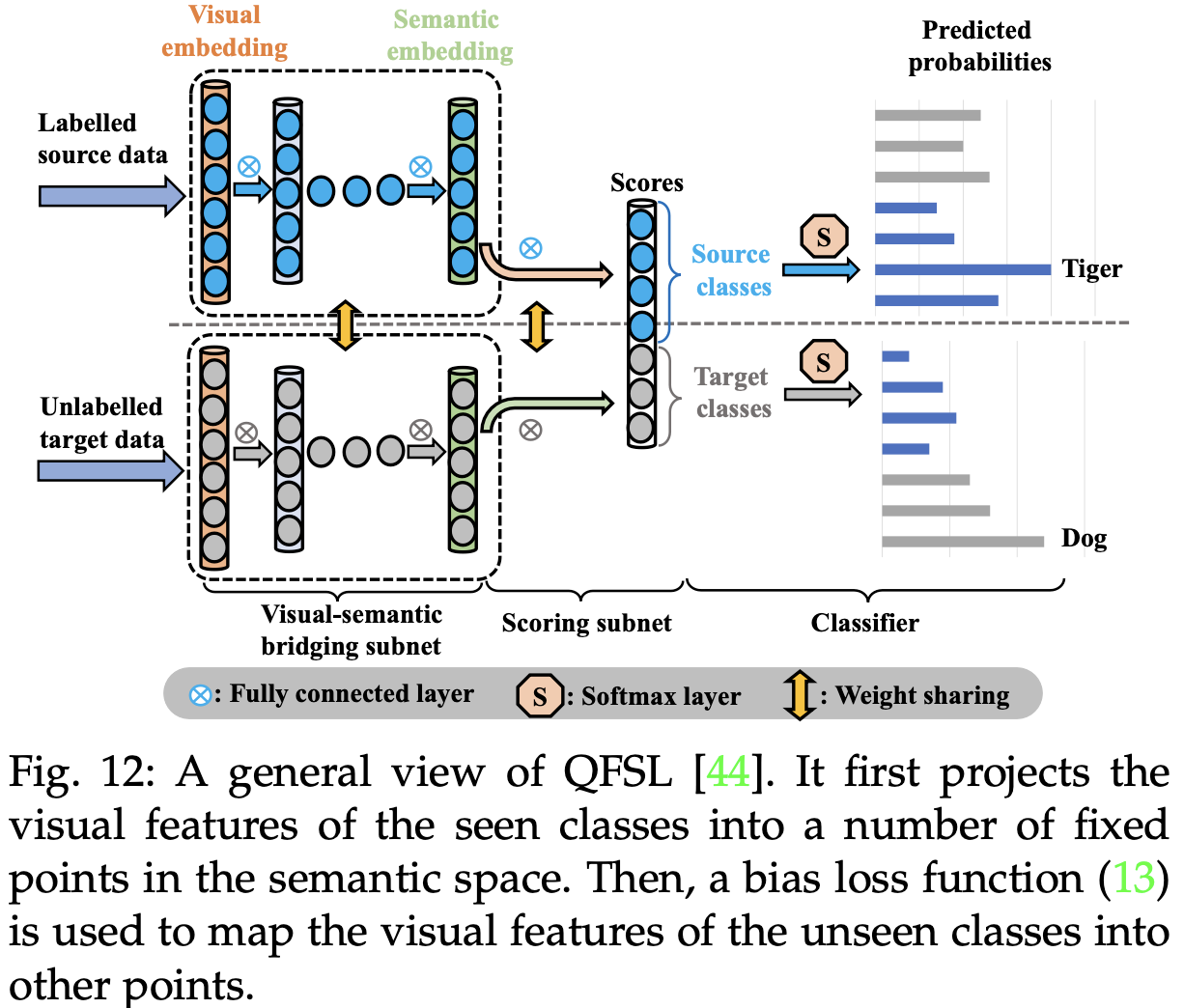
- Quasi-fully supervised learning(QFSL)
![Fig12]()
2. Generative-based methods
[ 5. Applications ]
- 최근 CV, NLP에 적용 → image classification, object detection, video processing, NLP
1. Computer vision
- image processing
- video processing
2. Natural language processing
[ 6. Discussions and Conclusions ]
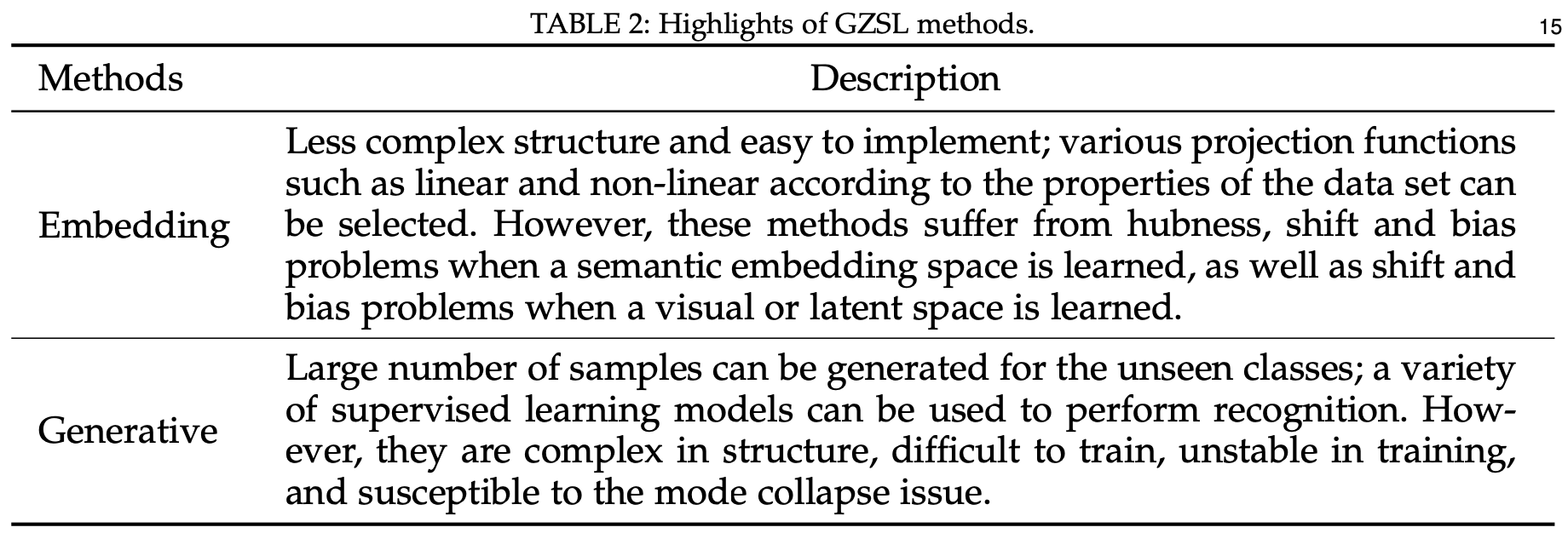
Highlights of GZSL methods
![Table2]()
- Embedding
- 장점
- 구조가 덜 복잡하고 구현하기 쉬움
- 데이터셋 속성에 따라 linear, non-linear 등 다양한 projection function 선택 가능
- 단점
- semantic embedding space 학습 시, hubness, shift, bias 문제
- visual/latent space 학습 시, shift, bias 문제
- 장점
- Generative
- 장점
- unseen class에 대한 많은 샘플 생성 가능
- 다양한 supervised model 사용 가능
- 단점
- 구조가 복잡하고 학습이 어려우며, 학습이 불안정해 mode collapse issue 존재
- 장점
- Embedding
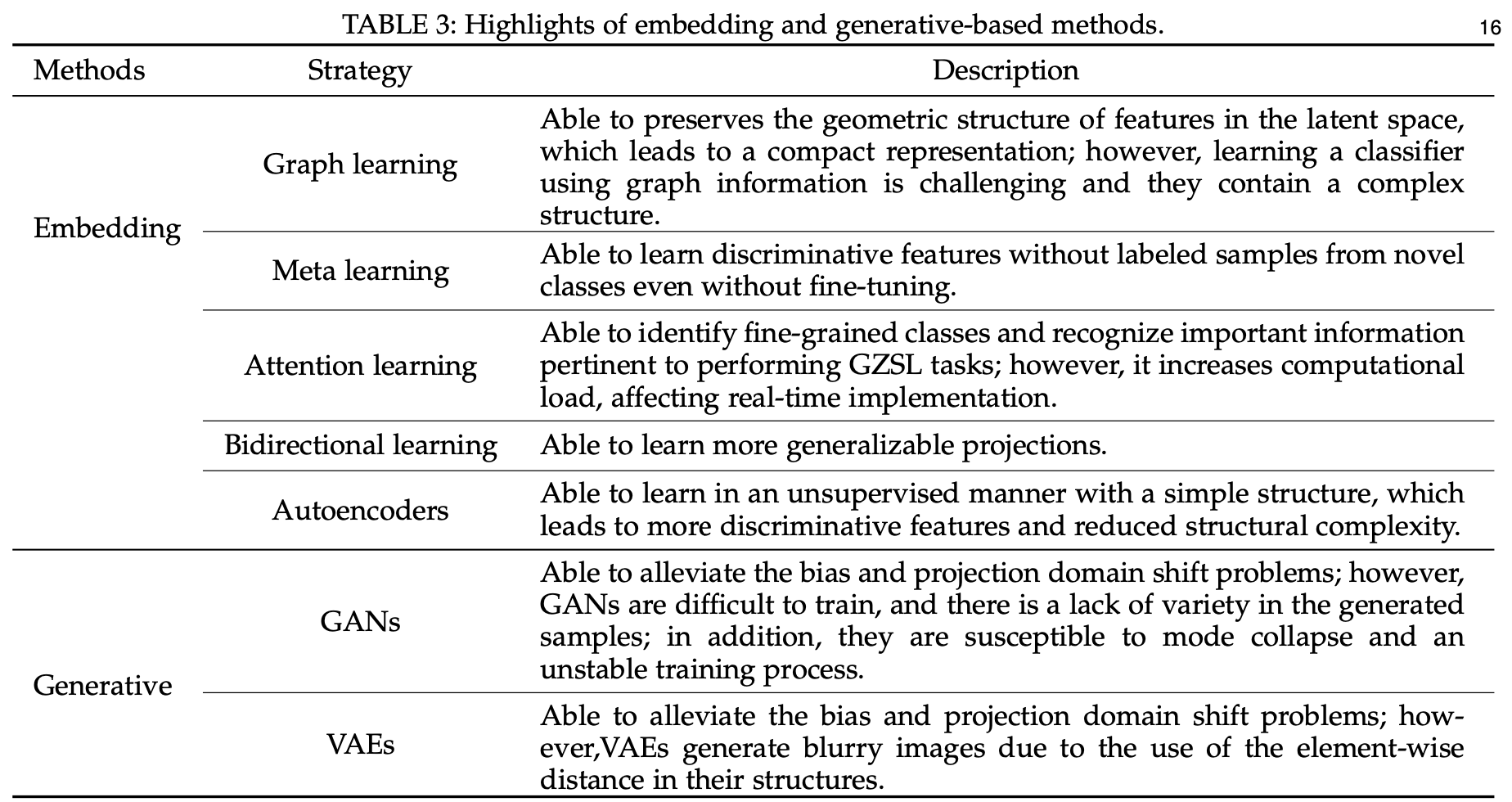
Highlights of embedding and generative-based methods
![Table3]()
A summary of ZSL methods

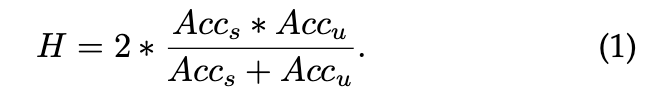
Comments powered by Disqus.